Trimester 2 Final MCQ
- Score
- Q22: Two robots in separate grids try to reach the goal
- Two grids are shown below. Each grid contains a robot represented as a triangle. Both robots are initially facing left. Each robot can move into a white or gray square, but cannot move into a black region.
- For each grid, the program below is intended to move the robot to the gray square. The program uses the procedure Goal_Reached ( ), which evaluates to true if the robot is in the gray square and evaluates to false otherwise.
- For which of the grids does the program correctly move the robot to the gray square?
- Q49: Crowd Flow Simulation
- Q50: Which algorithm runs in reasonable time
- Q22: Two robots in separate grids try to reach the goal
Score
Q22: Two robots in separate grids try to reach the goal
Two grids are shown below. Each grid contains a robot represented as a triangle. Both robots are initially facing left. Each robot can move into a white or gray square, but cannot move into a black region.
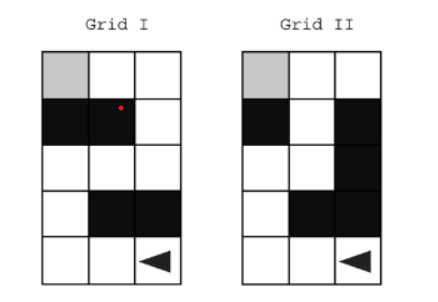
For each grid, the program below is intended to move the robot to the gray square. The program uses the procedure Goal_Reached ( ), which evaluates to true if the robot is in the gray square and evaluates to false otherwise.

For which of the grids does the program correctly move the robot to the gray square?
My Answer: Neither grid I nor grid II
Correct Answer: Grid I only
Explanation: In Grid I, the robot moves forward to the end of the bottom row, turns right twice, moves forward twice, turns right twice, moves forward until the end of the middle row, turns left twice, moves forward twice, turns left twice, and moves forward until Goal_Reached is true.
Q49: Crowd Flow Simulation
A city planner is using simulation software to study crowd flow out of a large arena after an event has ended. The arena is located in an urban city. Which of the following best describes a limitation of using a simulation for this purpose?
My Answer: The model used by the simulation software cannot be modified once the simulation has been used.
Correct Answer: The model used by the simulation software often omits details so that it is easier to implement.
Explanation: Simulations are limited by the model that is used. There may be many reasons for using a simplified model, including ease of implementation.
Q50: Which algorithm runs in reasonable time
A computer scientist is analyzing four different algorithms used to sort a list. The table below shows the number of steps each algorithm took to sort lists of different sizes.
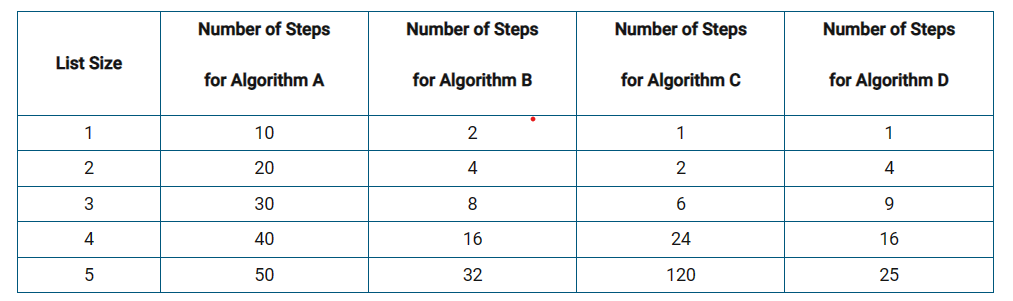
Based on the values in the table, which of the algorithms appear to run in reasonable time?
Select two answers.
My Answer: B and C
Correct Answer: A and D
Explanation: As the size of the list grows, the number of steps needed to sort the list grows at a linear rate, as the number of steps is equal to 10n for a list of size n. This is an example of a polynomial efficiency and indicates that the algorithm runs in a reasonable amount of time. The number of steps for this algorithm is equal to the length of the list squared, as the number of steps is equal to n2 for a list of size n. This is an example of a polynomial efficiency and indicates that the algorithm runs in a reasonable amount of time.