Trimester 2 MCQ Test Review/Corrections
- Proof of Completion
- Q11 Circuit with two logic gates
- Q13 old enough to drive but not to vote
- In a certain country, a person must be at least 16 years old to drive a car and must be at least 18 years old to vote. The variable age represents the age of a person as an integer.
- Which of the following expressions evaluates to true if the person is old enough to drive but not old enough to vote, and evaluates to false otherwise?
- Q25 Infinite repeat until loop
- Q30 use drawCircle to draw figure on a coordinate grid
- Q39 Robot in maze procedure MoveAndTurn
- The figure below shows a robot in a grid of squares. The robot is represented as a triangle, which is initially facing upward. The robot can move into a white or gray square but cannot move into a black region.
- Consider the procedure MoveAndTurn below.
- Which of the following code segments will move the robot to the gray square?
- Q40 Random movements for a robot
- Q49 What problems can be solved with algorithms
Proof of Completion
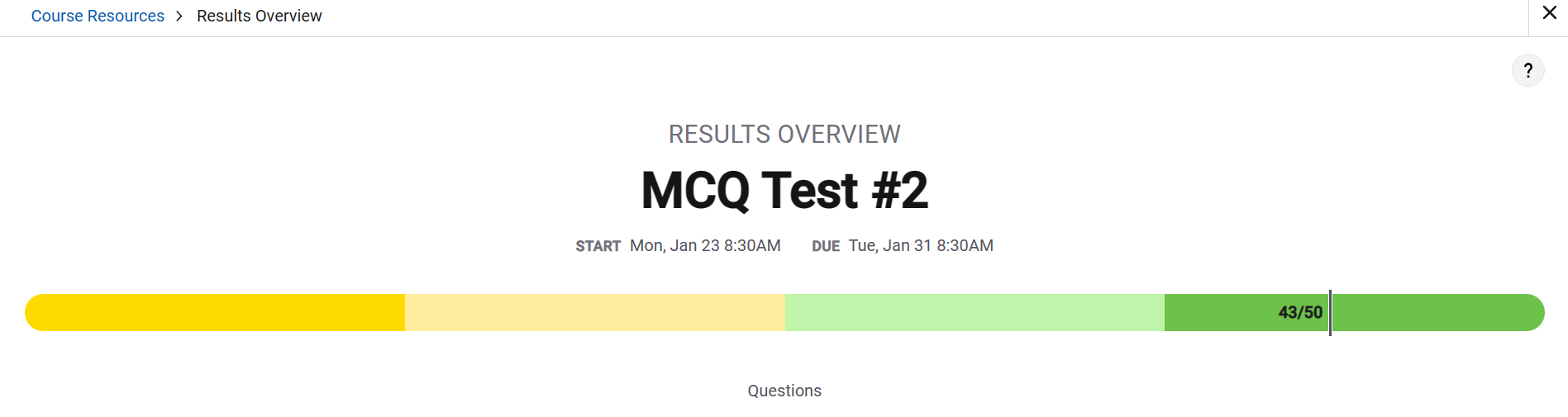
Q11 Circuit with two logic gates
The diagram below shows a circuit composed of two logic gates labeled OR and AND. Each gate takes two inputs and produces a single output.
If the inputs A and C are both true, which of the following best describes the output of the AND gate?
My response: The output will be true if input B is true; otherwise it will be false.
Correct Response: The output will be true no matter what the value of input B is.
Explanation: Because the value of input A is true, the resulting value coming out of the OR gate must be true. Because the value of input C is true, the resulting value coming out of the AND gate is true. The value of input B did not affect this result.
Q13 old enough to drive but not to vote
In a certain country, a person must be at least 16 years old to drive a car and must be at least 18 years old to vote. The variable age represents the age of a person as an integer.
Which of the following expressions evaluates to true if the person is old enough to drive but not old enough to vote, and evaluates to false otherwise?
- (age ≥ 16) AND (age ≤ 18)
- (age ≥ 16) AND (NOT(age ≥ 18))
- (age < 18) AND (NOT(age < 16))
My response: I and II only.
Correct Response: II and III only
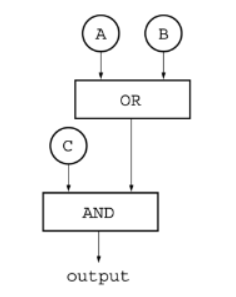
Q25 Infinite repeat until loop
Consider the following code segment.
Which of the following replacements for < MISSING CONDITION > will result in an infinite loop?
My response: j > 7
Correct Response: j = 6
Explanation: Because the value of the variable j starts at 1 and increases by 2, the value of j will always be odd. Thus the value of j will never equal 6. If < MISSING CONDITION > is replaced with the expression j = 6, the expression will always evaluate to false, and the loop will never end.
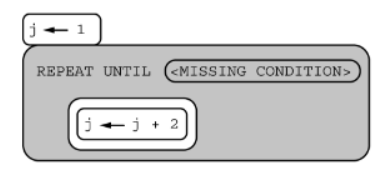
Q30 use drawCircle to draw figure on a coordinate grid
Consider the following procedure.

The drawCircle procedure is to be used to draw the following figure on a coordinate grid.
Which of the following code segments can be used to draw the figure? Select two answers.
Correct response:
x ← 4
y ← 1
r ← 0
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
r ← r + 1
y ← y + 1
drawCircle(x, y, r)
}
AND
x ← 4
y ← 4
r ← 3
REPEAT 3 TIMES
{
drawCircle(x, y, r)
y ← y - 1
r ← r - 1
}
Q39 Robot in maze procedure MoveAndTurn
The figure below shows a robot in a grid of squares. The robot is represented as a triangle, which is initially facing upward. The robot can move into a white or gray square but cannot move into a black region.
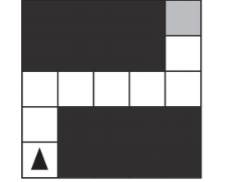
Consider the procedure MoveAndTurn below.
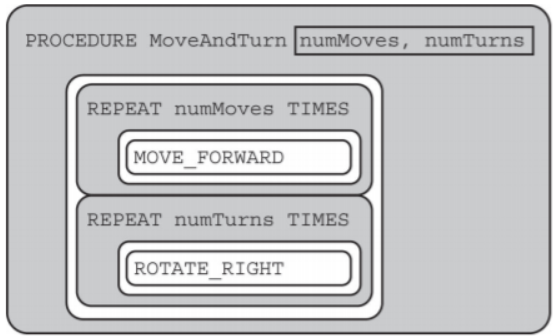
Which of the following code segments will move the robot to the gray square?
My response: Choice D has three boxes in a column. In choice D the top box reads MoveAndTurn, then 3,1 in a rectangle. The middle box reads MoveAndTurn, then 5, 3 in a rectangle. The bottom box reads MoveAndTurn, then 3, 0 in a rectangle.
Correct Response: Choice C has three boxes in a column. In choice C the top box reads MoveAndTurn, then 2,1 in a rectangle. The middle box reads MoveAndTurn, then 4, 3 in a rectangle. The bottom box reads MoveAndTurn, then 2, 0 in a rectangle.
Explanation: Because the value of the variable j starts at 1 and increases by 2, the value of j will always be odd. Thus the value of j will never equal 6. If < MISSING CONDITION > is replaced with the expression j = 6, the expression will always evaluate to false, and the loop will never end.
Q40 Random movements for a robot
The question below uses a robot in a grid of squares. The robot is represented as a triangle, which is initially in the center square of the grid and facing toward the top of the grid.
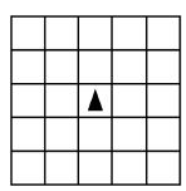
The following code segment is used to move the robot within the grid.

A gray square represents a possible final location of the robot after the code segment is executed. Which of the following represents all possible final locations for the robot?
My response: Each option shows a grid of squares with 5 rows and 5 columns. There is an upward-facing arrow representing a robot in the third square of row 3. The squares of the grid are as follows, from left to right and top to bottom: Row 1: white, white, gray, white, white. Row 2: white, white, gray, white, white. Row 3: gray, gray, white with robot facing upward, gray, gray. Row 4: white, white, gray, white, white. Row 5: white, white, gray, white, white.
Correct Response: Each option shows a grid of squares with 5 rows and 5 columns. There is an upward-facing arrow representing a robot in the third square of row 3. The squares of the grid are as follows, from left to right and top to bottom: Row 1: white, white, gray, white, white. Row 2: white, white, gray, white, white. Row 3: gray, gray, white with robot facing upward, gray, gray. Row 4: white, white, gray, white, white. Row 5: white, white, gray, white, white.
Explanation: The robot turns to the right one, two, or three times and then moves one or two squares forward. The possible final locations are to the right, below, or to the left of the starting position.
Q49 What problems can be solved with algorithms
Which of the following statements is true?
My response: Every problem can be solved with an algorithm for all possible inputs, but some of these algorithms have not been discovered yet.
Correct Response: Every problem can be solved with an algorithm for all possible inputs, but some of these algorithms have not been discovered yet.
Explanation: Every problem can be solved with an algorithm for all possible inputs, but some of these algorithms have not been discovered yet.